Big Data is a large volume of data
structured or unstructured, that, due to its size, complexity, and speed in generating new information, can be difficult to compile, manage, process, and analyze without the use of the appropriate technology.
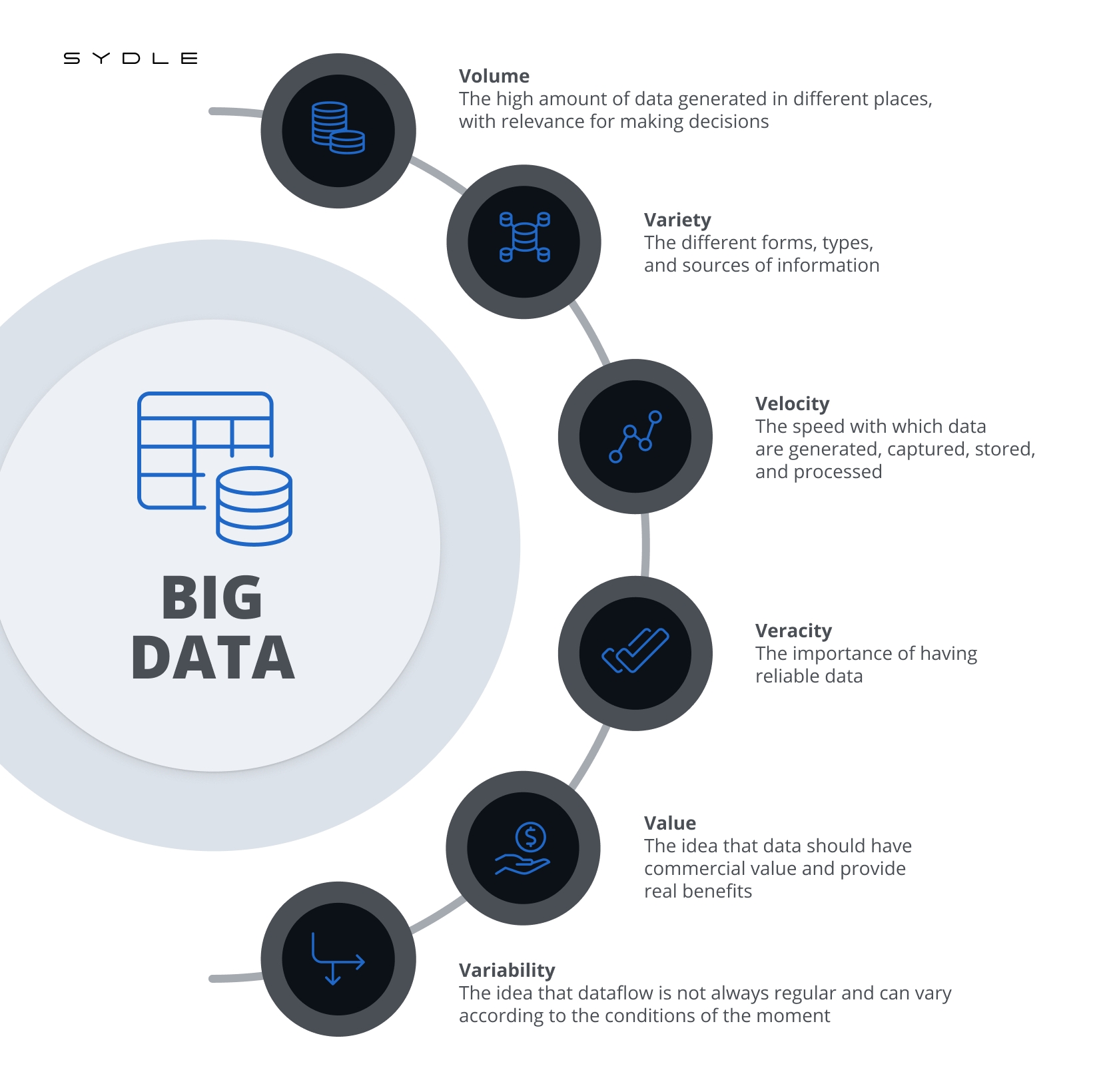
This data can be used for automatic learning in machine learning projects, predictive modeling, and many other analysis applications. The main features of this data are known as the 3 Vs:
- Volume: the high amount of data generated in different places, with relevance for making decisions.
- Variety: the different forms, types, and sources of information.
- Velocity: the speed with which data are generated, captured, stored, and processed.
Although those are its main features, there are still other important aspects that can be associated with the idea:
- Veracity: the importance of having reliable data.:
- Value :the idea that data should have commercial value and provide real benefits.
- Variability: the idea that dataflow is not always regular and can vary according to the conditions of the moment.
Big Data’s origins
Although it might seem to be something new, Big Data’s origins date back to the 60s and 70s, when the first data centers and relational database were created.
However, it was not until around 2005 that the data generated by the most used platforms such as Facebook and became evident. And it was only in 2006 that Hadoop was launched for storing and analyzing large data volumes and NoSQL (referring to non-relational databases) started to grow in popularity.
Moreover, the arrival of the IoT has also contributed to Big Data, since when more devices are connected to the internet, new data on use patterns are generated.
Even though Big Data is already bearing fruit, this is only the beginning, and there’s still much to come.
How does it work?
First, you must identify the sources where you will obtain your data before following the steps below:
- Integrate it process it and verify whether it is formatted and ready for use.
- Manage it organize its storage in either a physical or cloud server to make them available for analysis.
- Analyze it in other words, explore the data deeply in order to make new discoveries.
It’s important to understand in detail which data are available and what you’re looking for in them. This is how you’ll achieve a more efficient process.
Types of Big Data
.
1. Structured
Structured data are those that are organized and have a defined format. As a result, you can work with them more easily. One example of structured data is a calculation spreadsheet.
2. Unstructured
Unstructured data don’t have a defined form or structure. Aside from being very large, they bring a mix of different files, which makes it difficult to work with them. An example might be the result of a web search, in which you are shown text, images, and even videos.
3. Semi-structured
Semi-structured data have data in both forms: structured and unstructured. An example of semi-structured data might be an XML file.
Examples of Big Data
There are many sources of Big Data. They can be the data obtained from processing financial transactions, medical records, a business’s customer database, emails, social media databases, and so on.
However, computers can produce diverse data, for instance, industrial machines that generate files with operation logs, or devices with IoT technology.
What’s the importance of Big Data?
Big Data can improve business operations, offer more personalized service to customers, improve marketing campaigns and, in general, contribute to more efficient decision-making.
When a business knows how to use its data, it gains a competitive advantage over those that don’t, which makes it easier to grow and to increase market share.
Regardless of its sector, any business can use Big Data to improve its operations and better reach its audience.
Big Data in industry
Industry can use data to its advantage in many ways:
- Product development: You can build predictive models and anticipate customers’ demands, thereby reducing risks when releasing new products.
- Customer experience: When you compile data from consumers in many different contact channels, you can make personalized offers and manage problems proactively.
- Driven innovation: Knowing the data and analyzing trends helps improve financial planning and decision-making.
- Efficiency in operations: You can analyze and assess production through customer feedback and anticipate demands.
- Machine learning: You can use data to teach computers instead of programming them.
- Less fraud: You can identify patterns that help find fraud and suspicious activity.
- Predictive maintenance: You can foresee potential issues before they occur, saving on resources and optimizing equipment utilization.
What are the main challenges?
For all its benefits, there are still some challenges to overcome with Big Data. The great volume of data and the difficulty of storing it in an organized fashion requires the use of . What’s more, in general, data needs preparation if it is to be fully utilized.
There is a lot of available data that is not properly used. However, specialists in the topic are aware of this issue and have been working to deal with it better.
Big Data is just one of the technologies out there for maximizing business development, which is why we invite you to read our article on to discover how you can transform your business.




Comments
Post a Comment